NDP EyeCare | Dr. N D Patil | Dr. Gaurav Patil | Cataract | Glaucoma | Oculoplasty | LASIK
Our Latest Equipment is Best to keep your Vision perfect like Eagle!
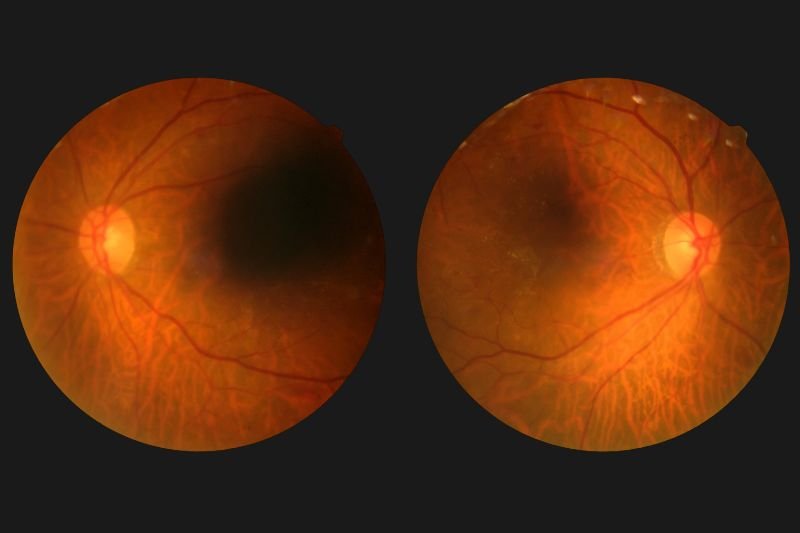
What is Diabetic Retinopathy Screening ?
Benefits of early screening
Detecting retinopathy before vision loss occurs
Reducing the risk of severe vision impairment
Guiding treatment such as laser therapy, injections, or surgery
Helping patients manage diabetes more effectively
Who Should Get Screened?
Diabetic retinopathy screening is recommended for:
All patients with Type 1 diabetes (starting 5 years after diagnosis)
All patients with Type 2 diabetes (starting at the time of diagnosis)
Pregnant women with diabetes (before conception and during pregnancy)
Regular follow-ups are advised every 6–12 months depending on your eye health and your doctor’s recommendations.
How is Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Done?
The screening process is simple, painless, and takes only a few minutes:
Eye Dilation: Eye drops are used to widen the pupils.
Retinal Photography/Imaging: A special camera captures detailed images of the retina.
Examination by an Eye Specialist: The retina is checked for any signs of blood vessel damage, swelling, or leakage.
Report & Recommendations: The results are explained, and follow-up tests or treatments are advised if needed.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Although diabetic retinopathy often develops silently, consult your eye doctor immediately if you notice:
Blurred or fluctuating vision
Dark spots or floaters
Difficulty seeing at night
Faded or washed-out colors
Sudden vision loss
Treatment Options for Diabetic Retinopathy
If detected early, diabetic retinopathy can be managed effectively. Treatment options include:
Laser Treatment (Photocoagulation): Seals leaking blood vessels and prevents abnormal growth.
Intravitreal Injections: Medications are injected into the eye to reduce swelling and stop abnormal blood vessel formation.
Vitrectomy Surgery: Removes scar tissue and blood from the eye in advanced cases.
How to Prevent Diabetic Retinopathy
While screening is essential, prevention plays an equally important role. You can lower your risk by:
Controlling blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol
Following a healthy diet and exercise routine
Quitting smoking and alcohol
Scheduling regular eye exams

